

News
SpaceX could provide satellite broadband service as early as 2020
Patricia Cooper, SpaceX’s VP of Satellite Government Affairs, provided a statement to the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation regarding SpaceX’s broadband satellite constellation ambitions.
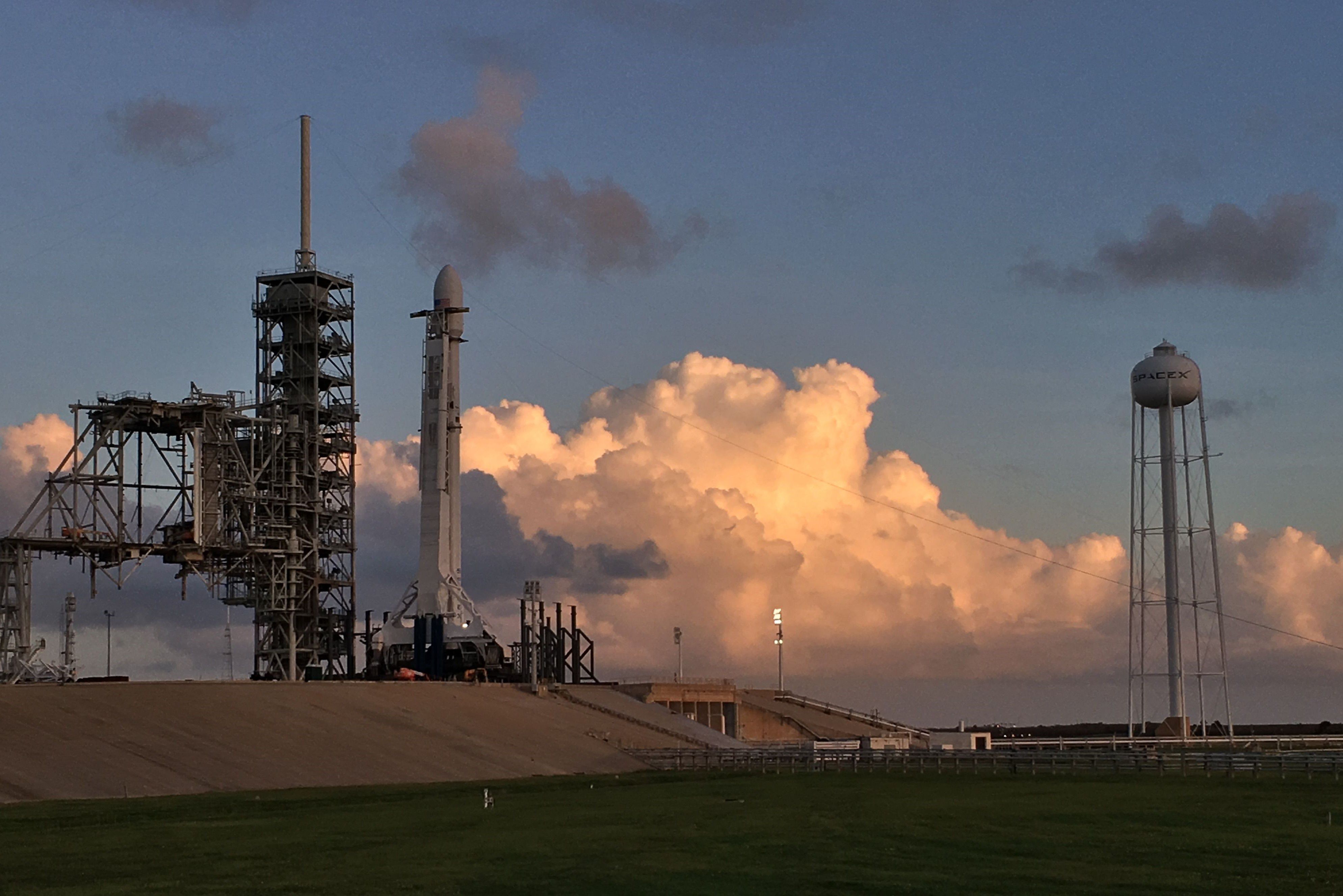
Of note, Cooper reiterated on Wednesday that SpaceX intends to launch two prototype satellites into orbit within the next few months, and further suggested that an operational Starlink launch campaign is tentatively scheduled to begin in 2019. She also noted that the company’s initial ~4000 satellite constellation is meant to be launched over a space of five years, with limited service beginning in 2020 or 2021 once ~800 satellites have been placed in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
While officially unconfirmed, FCC filings have for several months suggested that SpaceX was hoping to launch its first prototype communications satellites relatively soon, and Cooper’s comments indicate that those prototypes will be launched in late 2017 or early 2018. According to those documents, the reported orbit of SpaceX’s prototype Microsats fits perfectly with the planned orbit of PAZ, a Spanish Earth imaging satellite, which is scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base, CA on January 30 2018.

SpaceX’s Starlink satellite constellation efforts could provide the company with valuable experience that can be applied around Mars. (unofficial logo by Eric Ralph)
More experimental satellites are likely to follow the launch of Microsat 2A/2B, although SpaceX’s aggressive technology development strategy could preclude future experimental launches if all goes as planned. If SpaceX hopes to begin operational launches by 2019 and launch ~800 satellites no later than 2021, the company will have to both settle on a finalized design and rapidly expand its satellite manufacturing capabilities in the near term.
Nevertheless, Cooper unambiguously stated that SpaceX is not currently pursuing outside investment for Starlink research and development. This suggests the company is relatively confident in its near and long term strategies for rolling out its satellite broadband constellation, despite its aggressive schedule.
OneWeb, also pursuing a large broadband constellation, plans to effectively mirror SpaceX’s current strategy approximately one year before, with initial launches in 2018 and limited service in 2019. As such, OneWeb’s success or lack-thereof will almost certainly inform SpaceX’s own strategy, although the technologies being pursued by both companies are somewhat different, as are the launch opportunities for each company.
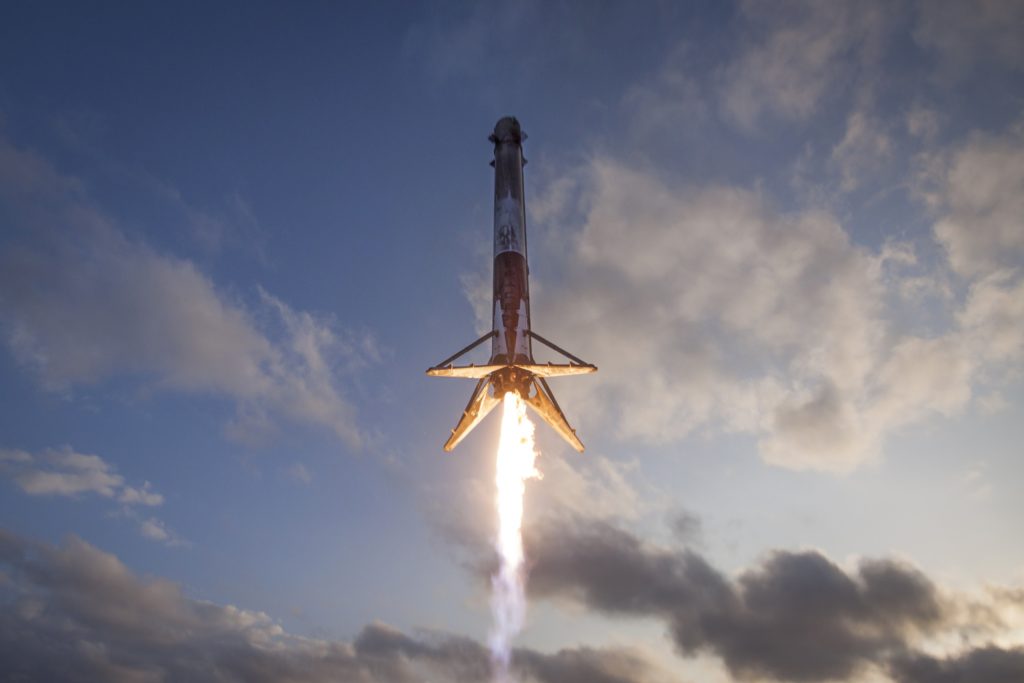

After launching SES-10, the first stage was recovered for a second time aboard the drone ship OCISLY. Reuse will be a major boon for SpaceX’s internal satellite efforts. (SpaceX)
As a vertically-integrated launch provider with considerable expertise in orbital rocketry, SpaceX undoubtedly has the upper hand over all competitors simply because it can quite literally launch at cost, bypassing the relative difficulty of procuring vast numbers of commercial launches. Combined with SpaceX’s ability to unilaterally fly on refurbished launch vehicles, it is all but impossible that competing broadband constellation providers can meet a similar level of cost efficiency while purchasing market-value launches.

News
Tesla rolls out latest Safety Score update—Here’s what’s new
Tesla’s latest Safety Score update drops one highly criticized factor, while adding weight to pieces like speeding, follow distance, and more.

Tesla has officially started rolling out a new version of its insurance program’s Safety Scores beta, improving upon a few different metrics that make up the index.
As detailed on the Tesla Insurance web page, the company has updated its Safety Scores to beta version 2.2 from the previous version 2.1. The update primarily includes improvements to how Excessive Speeding is measured, along with the removal of Forward Collision Warnings (FCW) from the formula.
In addition, Tesla has slightly increased the values of related factors such as Hard Braking and Unsafe Following Time in the v2.2 formula, perhaps in an attempt to help accommodate some of the situations previously covered by the FCW rating.
READ MORE ON TESLA INSURANCE: Tesla launches insurance discount for FSD users in these two states
Tesla’s Safety Scores are used to determine premium rates for buyers of the company’s in-house insurance program, except in California, where privacy laws prohibit the use of real-time driving data to determine premiums. The company also says that its latest formula for Safety Scores were generated using over 22 billion miles of fleet data from its cars, while the company plans to continue improving the formula as more data comes in.
At this time, Tesla Insurance is available in the following 12 states, though Safety Scores aren’t available in California for the aforementioned reason:
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Illinois
- Maryland
- Minnesota
- Nevada
- Ohio
- Oregon
- Texas
- Utah
- Virginia
You can see the factors that make up Tesla’s Insurance Safety Scores below or on its website here, along with the specific formula that makes up a drivers’ 0 to 100 Safety Score.
Hard Braking

Credit: Tesla
Hard braking is defined as backward acceleration, measured by your Tesla vehicle, in excess of 0.3g. This is the same as a decrease in the vehicle’s speed larger than 6.7 mph, in one second. Hard braking is introduced into the Safety Score Beta formula as the proportion of time where the vehicle experiences backward acceleration greater than 0.3g as a percentage of the proportion of time the vehicle experiences backward acceleration greater than 0.1g (2.2 mph in one second). Hard braking while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. For vehicles with Autopilot computer 3.0 or greater, braking while the vehicle detects yellow traffic lights is also not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. If the vehicle is unable to detect a yellow traffic light at the time of the hard braking, the event will impact your Safety Score. The percentage shown in the app is the proportion of time spent braking done with excessive force when driving and Autopilot is not engaged. The value is capped at 5.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Aggressive Turning

Credit: Tesla
Aggressive turning is defined as left/right acceleration, measured by your Tesla vehicle, in excess of 0.4g. This is the same as an increase in the vehicle’s speed to the left/right larger than 8.9 mph, in one second. Aggressive turning is introduced into the Safety Score Beta formula as the proportion of time the vehicle experiences left or right acceleration greater than 0.4g as a percentage of the proportion of time the vehicle experiences left or right acceleration greater than 0.2g (4.5 mph in one second). Aggressive turning while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. The percentage shown in the Tesla app is the proportion of time spent turning with excessive force when driving and Autopilot is not engaged. The value is capped at 13.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Unsafe Following

Credit: Tesla
Your Tesla vehicle measures its own speed, the speed of the vehicle in front and the distance between the two vehicles. Based on these measurements, your vehicle calculates the number of seconds you would have to react and stop if the vehicle in front of you came to a sudden stop. This measurement is called “headway.” Unsafe following is the proportion of time where your vehicle’s headway is less than 1.0 seconds relative to the time that your vehicle’s headway is less than 3.0 seconds. Unsafe following is only measured when your vehicle is traveling at least 50 mph and is incorporated into the Safety Score Beta formula as a percentage. Unsafe following while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. The percentage shown in the Tesla app is the percentage of unsafe following when driving and Autopilot is not engaged. The value is capped at 63.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Excessive Speeding
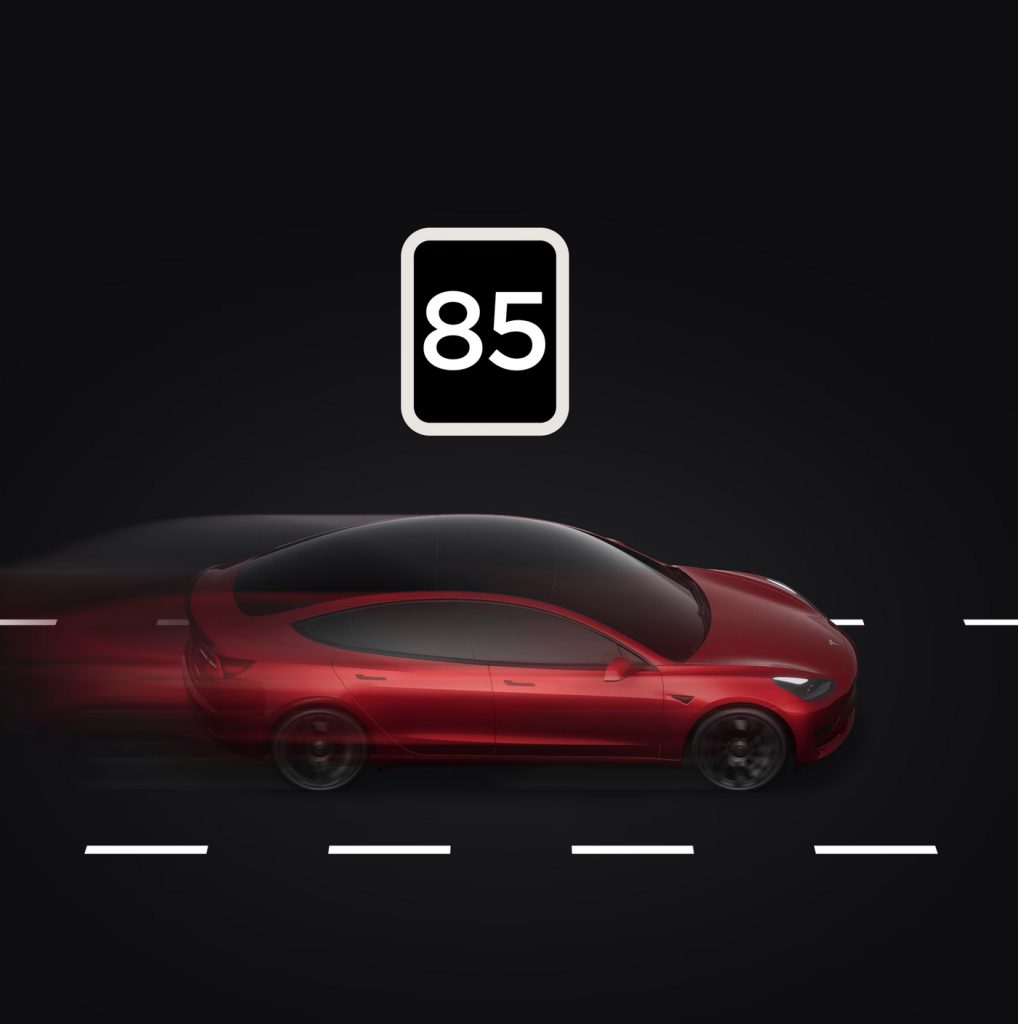

Credit: Tesla
Excessive Speeding is defined as the proportion of time spent driving in excess of 85 mph or driving 20% faster than the vehicle in front of you, when that vehicle is going over 25 mph and is within 100 meters of your vehicle. This value is expressed as a percentage of total driving time and is capped at 10.0% in the Safety Score Beta formula. Speeding while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula.
Late-Night Driving

Credit: Tesla
Late-Night Driving is defined as the number of seconds you spend driving at night (11 PM – 4 AM) divided by the number of seconds you spend driving total during the day and night. Due to the variable risk level associated with driving during each late-night hour, each hour is weighed differently, and driving at each hour will affect your Safety Score differently. For example, driving at 11 PM will not affect your Safety Score as heavily as driving at 2 AM. Drive sessions that span two days will apply to the day the trip ends. Late-Night Driving includes all driving at night (11 PM – 4 AM) including any driving done on Autopilot. The value is capped at 14.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Forced Autopilot Disengagement

Credit: Tesla
The Autopilot system disengages for the remainder of a trip after the driver has received three audio and visual warnings. These warnings occur when your Tesla vehicle has determined that the driver has not applied sufficient resistance to the steering wheel or has become inattentive. Forced Autopilot Disengagement is introduced into the Safety Score Beta formula as a 1 or 0 indicator. The value is 1 if the Autopilot system is forcibly disengaged during a trip, and 0 otherwise.
Unbuckled Driving

Credit: Tesla
Unbuckled Driving is defined as the proportion of time spent driving above 10 mph without fastening the driver’s seatbelt in a Tesla vehicle, as a percentage of time spent driving above 10 mph. The value shown in the Tesla app is the proportion of time driven at a speed over 10 mph, without buckling the driver’s seatbelt, as a percentage of time spent driving over 10 mph. The value is capped at 31.7 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Tesla’s formula for Safety Score beta v2.2
Tesla takes the formula pictured below, dubbed its Predicted Collision Frequency (PCF), and converts it into the 0 to 100 version 2.2 Safety Score it assigns based on driver behavior. The 2.1 Safety Score formula can also be seen on the Tesla Insurance page, though the below formula is for the newly launched version 2.2.
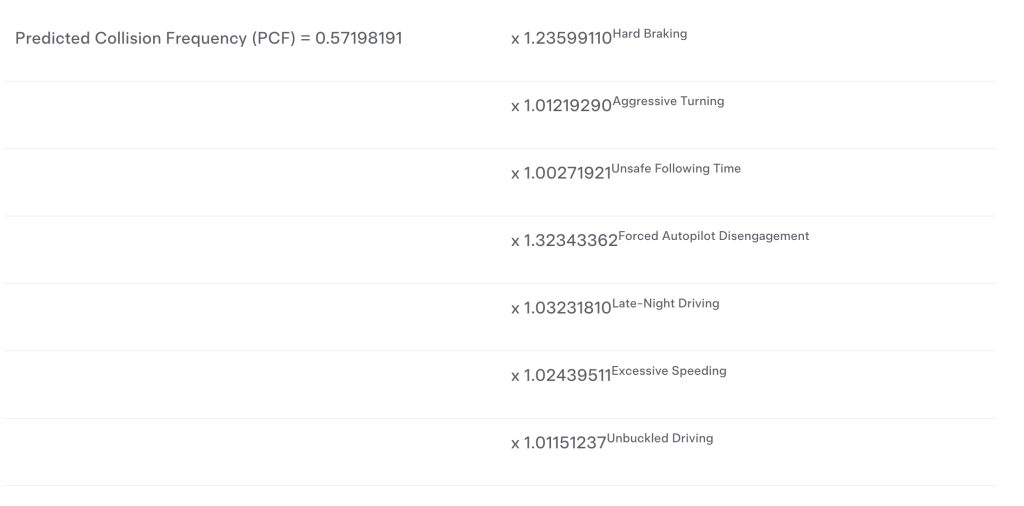
Credit: Tesla
News
Tesla celebrates key milestone for 4680 battery cell production cost
Tesla produces in-house 4680 battery cells at its Gigafactory in Texas, along with getting them from outside suppliers.

Tesla has highlighted an important 4680 battery cell milestone in recent weeks, noting that its Texas manufacturing team for the hardware has scaled production enough to outpace the cost-effectiveness of outside suppliers.
During Tesla’s first-quarter all-hands-on-deck meeting held a few weeks ago, CEO Elon Musk shared a number of recent milestones. One of them, as was also reiterated after the meeting by Michael Guilfoy, Tesla’s Giga Texas Director of Cell Manufacturing, is the fact that the company’s in-house 4680 battery cells have earned their place as the lowest-cost battery cell produced per kWh.
Musk also pointed out during the meeting that the achievement is particularly impressive, given that many of the company’s suppliers dedicate all or most of their businesses to battery cell manufacturing, while Tesla focuses on several other business sectors and still managed to surpass the milestone.
Check out Guilfoy’s full message below, as posted on LinkedIn, or watch Tesla’s Q1 all-hands meeting below that.
Been waiting to acknowledge this great achievement by Tesla’s 4680 Cell Manufacturing team since the end of last year….but as Elon announced last night, our Cell Manufacturing team in Texas reached a huge milestone at the end of 2024 with becoming the lowest cost per kWh battery cell producer for Tesla! The grit, determination, and passion of our team is unbelievable in helping deliver our mission.
Big thank you to our entire engineering and production teams for making this happen!! It’s the greatest honor of my career to lead this team and make such an impact in our mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
And we aren’t done yet! 2025 will have more big milestones with fully ramped dry battery electrode manufacturing to deliver even more cost efficiency. Exciting teams continue to be ahead. Cheers to this world-class team!
READ MORE ON TESLA’S 4680 BATTERY CELLS: Tesla working on four dry cathode 4680 battery variants: The Information
Although Tesla also sources its 4680 batteries from multiple other suppliers, including Panasonic and LG Energy Solution, the company has also been working to scale up in-house production of the cells over the past few years. In September, Tesla officially surpassed a milestone of producing 100 million 4680 battery cells, after surpassing 50 million last June, and exceeding 20 million in October 2023.
Tesla initially unveiled the 4680 battery cell during a 2020 “Battery Day” event, during which it explained the cost and efficiency benefits of the battery size in comparison with the 2170 form factor.
News
Tesla Europe shares FSD test video weeks ahead of launch target
Tesla aims to launch Supervised Full Self-Driving in European markets in the coming weeks, though engineering tests are well underway.

Tesla has shared a new video showing off some of its tests of Supervised Full Self-Driving (FSD) in Europe, as the company aims to gain regulatory approval in the region in the coming months.
In a post on the Europe and Middle East X account on Saturday, Tesla shared a video of some of its tests in what appears to be Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Although Tesla is aiming to launch the software in new markets across Europe and the Middle East this year, the video notes that the drives are still “engineering test drives,” rather than the system being launched yet in those markets.
“FSD Supervised in Europe, pending regulatory approval,” the account writes.
In fine print at the beginning of the video, Tesla also writes the following disclaimer:
FSD (Supervised) engineering test drive – these recordings were made in a prototype vehicle driven by a safety driver during test phase. Features on display require active driver supervision and do not make the vehicle autonomous. Activation and use is subject to regulatory approval.
You can see the full two-minute video below.
FSD Supervised in Europe, pending regulatory approval pic.twitter.com/PYkcATjSUN
— Tesla Europe & Middle East (@teslaeurope) April 5, 2025
READ MORE ON TESLA FSD IN EUROPE: Tesla’s Full Self-Driving faces a new hurdle in UK rollout plans
Tesla has been performing closed testing of FSD systems in Europe for years, and Elon Musk said during the company’s Q4 earnings call that it’s expecting to gain approval during an upcoming assembly.
In order to start deploying the system publicly, Tesla will ultimately have to be approved by the Dutch RDW, the transportation division overseeing self-driving vehicle regulation, which will then present the company’s permit submission to the European Union (EU) in May.
You can see a few details on the Netherlands government’s approach to and management of self-driving vehicle permits here.
The video also comes after Tesla launched FSD Supervised in China and Mexico over the past few months, and after Elon Musk and others have highlighted how many regulations the company is subject to in European markets.
Upon his departure from Tesla in October, former Global Vehicle Automation and Safety Policy Lead Marc Van Impe said that certain features of a regulation expected to accelerate the regulation of self-driving vehicles could be delayed, “possibly until 2028,” going on to warn that this could significantly delay the launch of FSD Supervised.
Former Tesla executive warns of delays to European ADAS regulations
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoTesla rolls out new, more affordable trim of the Model Y Juniper in U.S.
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla CEO Elon Musk’s simple message to vandals
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoTesla shares Optimus’ improved walk in new update video
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla vandal who lit Las Vegas repair center on fire arrested
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoElon Musk clarifies Trump tariff effect on Tesla: “The cost impact is not trivial”
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Giga Berlin director responds to anti-Musk criticism
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla US Gigafactories shields from Trump’s 25% Tariffs
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoMusk says xAI has acquired X in $33 billion stock deal







